- HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language
- HTML is the standard markup language for creating Web pages
- HTML describes the structure of a Web page
- HTML consists of a series of elements
- HTML elements tell the browser how to display the content
- HTML elements label pieces of content such as “this is a heading”, “this is a paragraph”, “this is a link”, etc.
A Simple HTML Document
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>My First Heading</h1>
<p>My first paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
Example Explained
- The
<!DOCTYPE html>declaration defines that this document is an HTML5 document - The
<html>element is the root element of an HTML page - The
<head>element contains meta information about the HTML page - The
<title>element specifies a title for the HTML page (which is shown in the browser’s title bar or in the page’s tab) - The
<body>element defines the document’s body, and is a container for all the visible contents, such as headings, paragraphs, images, hyperlinks, tables, lists, etc. - The
<h1>element defines a large heading - The
<p>element defines a paragraph
What is an HTML Element?
An HTML element is defined by a start tag, some content, and an end tag:<tagname>Content goes here…</tagname>
The HTML element is everything from the start tag to the end tag:
<h1>My First Heading</h1>
<p>My first paragraph.</p>
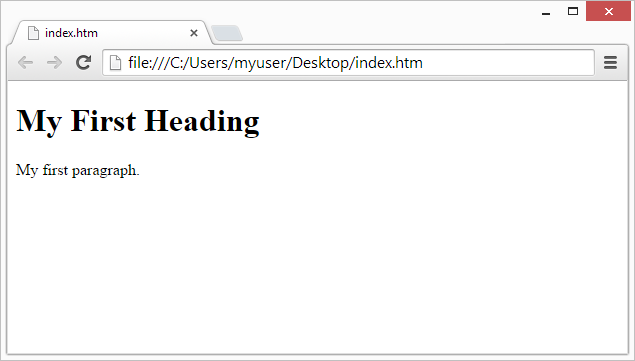
Web Browsers
The purpose of a web browser (Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Safari) is to read HTML documents and display them correctly.
A browser does not display the HTML tags, but uses them to determine how to display the document:
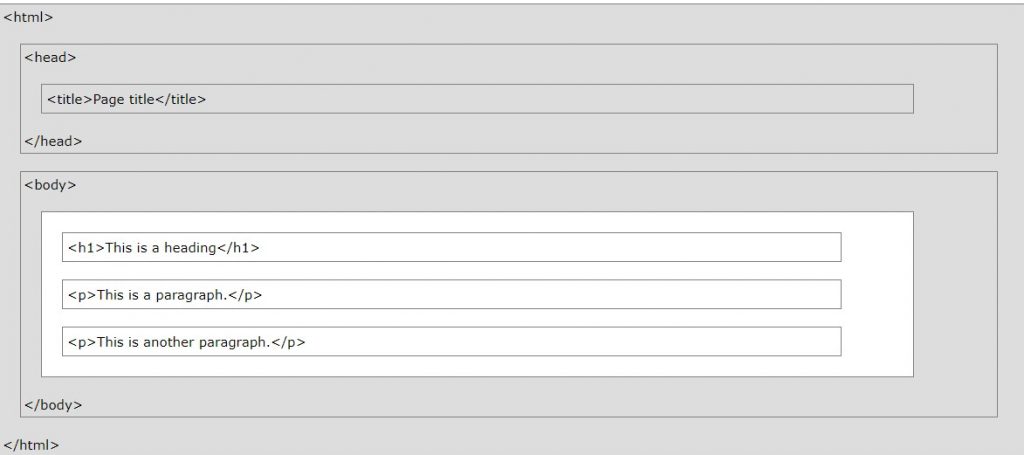
HTML Page Structure
Below is a visualization of an HTML page structure:
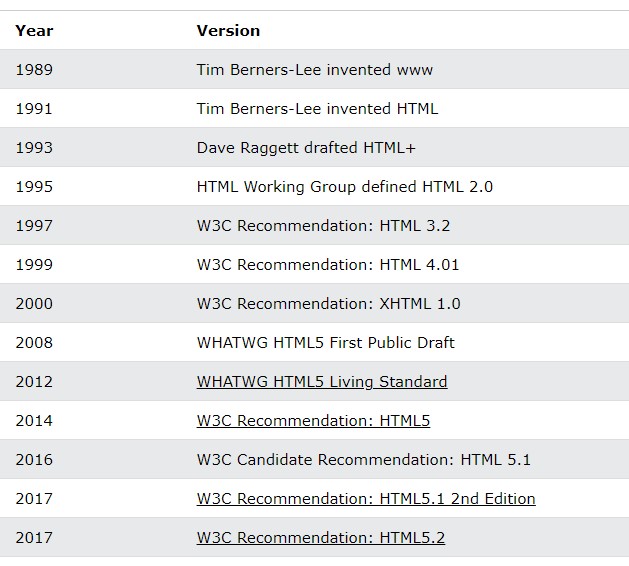
HTML History
Since the early days of the World Wide Web, there have been many versions of HTML: